[ad_1]
“These critical systems need to deliver upwards of 99.999% availability, which makes prolonged maintenance and unplanned downtime unacceptable,” said the firm. Hot-swapping is widely employed to keep these systems running, however today’s sensitive high-speed serial communication busses were not designed to facilitate hot-swapping.”
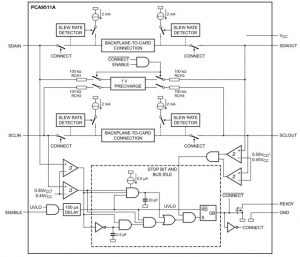
The chip, the PI6ULS5V9511A provides a bidirectional buffer between the card’s SDA and SCL signals and the system’s live busses.
Internal control circuits detect bus activity, allowing the PI6ULS5V9511A to maintain electrical isolation between the live system and the line-card until it identifies a stop command or the bus is idle, at which point it switches in the signals without causing bus contention or data disruption – eliminates the potential for bus corruption during card insertion and removal, according to Diodes.
Rise-time accelerators are used to meet rise-time requirements on all data pins, while pre-charge minimises the current required to overcome the parasitic capacitance present on the data pins.
Because the PI6ULS5V9511A provides drive capabilities it is also an effective buffer for increasing the fan-out of an I2C/SMBus port.
There is an active-high ‘ready’ pin which indicates to the system when connection is established, as well as an active-high ‘eanable’ pin that can be used to isolate the two sides of the bidirectional buffer.
ESD protection exceeds 4000V HBM, as specified in the JESD22-A114 JEDEC Standard.
The chip comes in a choice of three packages: SO-8(W), MSOP-8(U), and the smaller UDFN-8(ZW).
[ad_2]
Source link